PBX Telephone System
"The Communication Network breaks the boundaries of the world and changes business life in the world"
PBX is a device with switching technology which is a private telephone network system that allows internal and external communications as a means to connect and manage incoming and outgoing telephone communications efficiently and effectively.
Most people question whether there is any difference between PABX and PBX.
The two terms above currently have the same meaning, because PBX is now far advanced and the two terms have no difference. PABX is a different type of PBX with the term “automatic”. PBX is a “private branch exchange”, while PABX is a “private auto branch exchange”. PBX requires a switchboard operator to connect external callers to the network or vice versa and is done manually. Outside callers should know which number to call directly.
In its development was born the automatic telephone system that is PABX. Users can dial extension numbers to make internal calls without an operator. So functionally the PBX is the same as the PABX.
The advantages of using a PBX are;
- Ease of transferring internal and external calls to other destination stations.
- Can make conference calls.
- Can record every call
- Have the flexibility to connect with other systems both within the network and outside the network.
- The network has privacy because all conversations are encrypted which is a default PBX to protect all conversations even without a VPN.
- And many other features recently owned by PBX
In accordance the technological developments, PBX consists of several types including;
- Analogue PBX; A switching technology that utilizes analog signals (converting voice into pulses or continuous electrical signals) to connect the old Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS) telephone service lines to the public telephone network (PTSN) via a copper loop. This type of analog PBX is to produce a clear voice, low cost and can fulfill communication between two destination stations, especially internal network communication. Intended for small networks.
- Digital PBX; (Digital Private Branch Exchange) A modern PBX that uses digital methods (voice is converted by pulse-code modulation to a stream of binary pulses) is another generic term for IP-PBX or VoIP PBX.
- Internet Protocol (IP PBX); Also called VoIP PABX, this PABX system is an improved version of the analog PABX. It provides more features and enables connectivity between multiple locations. VoIP or IP PBX uses internet protocol (IP) that connects one station to another. IP PBX provides access to unified communications features such as messaging, and video conferencing, which analog PABX systems do not have. Internet Protocol PABX uses trunking session initial protocol (SIP) for telephone services in office networks, where communications with each other and external clients are made via the Internet.
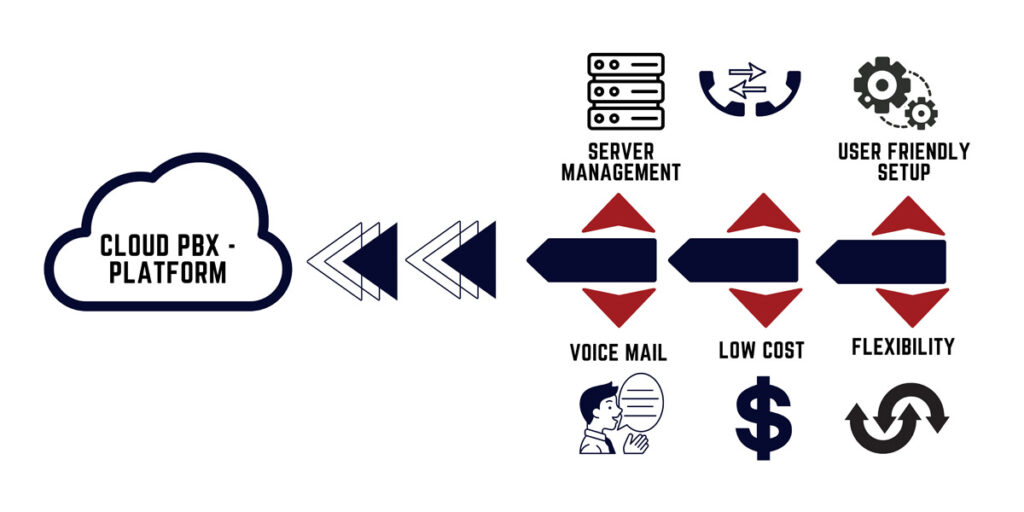
- Cloud PABX; Also known as virtual or hosted PABX, cloud PABX uses internet protocol technology to receive calls without any equipment installed in the location doing the communication. Incoming and outgoing call services through packet data or public telephone networks. Cloud PABX is managed with a web browser. with the cloud, PABX can control all call forwarding, call routing, call recording, music on hold, and auto attendant from anywhere. Cloud PABX hosted PABX, virtual phone system, virtual PABX, VoIP phone system, VoIP PABX, online phone system (Internet Protocol) PABX, hosted PABX, or by any other name. Cloud-based private branch exchange (PABX) is a telephony solution using a softphone and the Internet for phone calls. A softphone is a software application that is installed on an internet-connected device to make telephone calls. The softphone software is a user-friendly interface that works just like a normal telephone. This interface allows users access to calls and all the features included with their VoIP solution.